The ability to use a computer to automatically recommend a complete and reasonable organic chemical synthesis route, that is, Computer-Aided Synthesis Planning (CASP) has always been the vision of chemists. The CASP method is based on the inverse synthesis analysis method proposed by E. J. Corey and predicts the synthesis route based on chemical reaction rules. Chemical reaction rules are divided into two categories: expert summary rules and computer automatic extraction rules. However, manual extraction of reaction rules is time-consuming and labor-intensive, making it difficult to meet the ever-increasing demand for new organic chemical reactions, and it cannot be used to predict new chemical reactions.
In recent years, artificial intelligence has been used to predict the products of chemical reactions, and for reverse synthesis analysis, and is expected to break through the bottleneck of existing reverse synthesis analysis technology. At present, the starting point of artificial intelligence-assisted compound synthesis route planning is still a large-scale reaction database and artificially extracted reaction rules. The team of Professor Lai Luhua and Pei Jianfeng used artificial intelligence natural language processing and developed a single-step reverse synthesis analysis method that only needs to input the target product molecule to predict the product to the precursor. Good accuracy was obtained in the prediction of step-reverse synthesis reaction.
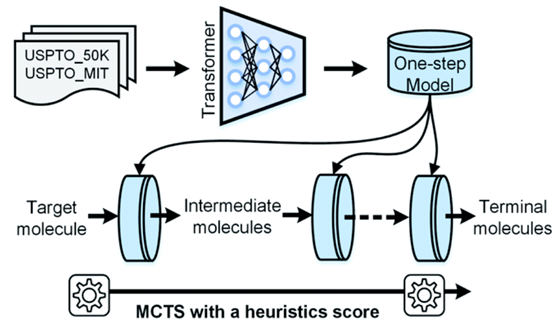
Figure 1. AutoSynRoute workflow. A single-step reaction prediction model was developed using the Transformer framework. The single-step reaction prediction model was used to convert the target molecule into a simpler intermediate molecule. Repeating this process can obtain the terminal raw material molecule. AutoSynRoute uses the Monte Carlo tree search method (MCTS) based on heuristic scoring.
On the basis of single-step reverse synthesis reaction prediction, the automated compound organic synthesis route planning tool AutoSynRoute was further developed (Figure 1). AutoSynRoute first heuristically scores the predicted multiple candidate reactions, and then integrates the Monte Carlo Search Algorithm (MCTS) to search for the best combination of reaction routes. AutoSynRoute can reproduce the compound synthesis routes reported in the literature, showing the application potential in the automatic planning of compound synthesis routes.
AutoSynRoute enables automatic analysis of compound reverse synthetic routes that are not based on chemical reaction rules. This work was first published on the preprint platform Chemrxiv in May 2019, and was recently published in the journal Chemical Science under the title "Automatic Retrosynthetic Route Planning Using Template-Free Models"(https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2020/sc/c9sc03666k). Professor Lai Luhua and Professor Pei Jianfeng are the corresponding authors of the paper, and Lin Kangjie, a PhD student in the School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, and Xu Youjun, a postdoctoral fellow, are co-first authors of the paper. Lin Kangjie and Xu Youjun won the 2019 Merck Cup reverse synthesis reaction prediction contest.
This work received funding and support from major new drug creation technology major projects, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the National Key R & D Program. The high-performance computing platform of the Peking University-Tsinghua Life Science Joint Center provided part of the computing resources for this research.